Research into autonomous delivery vehicle: Probe from single vehicle, fleet, to urban operation
Autonomous delivery is bifurcated into indoor autonomous delivery and outdoor autonomous delivery. Correspondingly, there are indoor autonomous delivery vehicles (also known as "indoor delivery robots") and outdoor ones.
Indoor autonomous delivery market
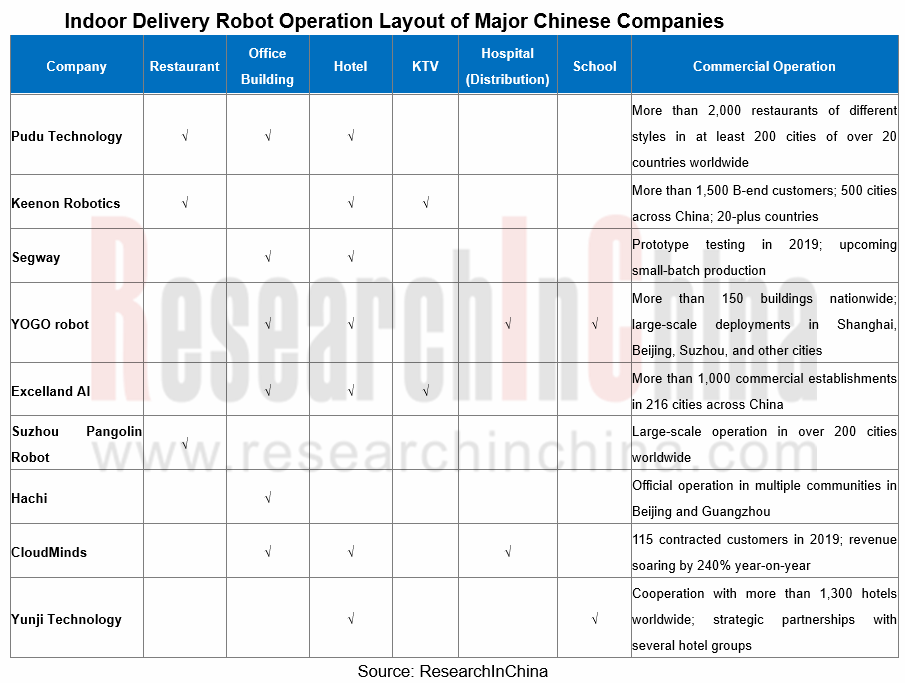
Up to date, indoor autonomous delivery robots have been available in restaurants, hotels, office buildings, hospitals, Internet cafes, KTVs, and shopping malls, and has got vigorously promoted amid “contactless” services for the prevention and control of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, being quite a boon for faster deployment and operation of intelligent equipment such as indoor autonomous delivery robot. For instance, many catering companies such as Country Garden Robot Restaurant, Haidilao, De Zhuang, Xiabu Xiabu, Dadong, Hong Kong Maxim's, etc. have begun to use autonomous delivery robots to serve dishes in their stores to save labor costs and improve the security of meals.
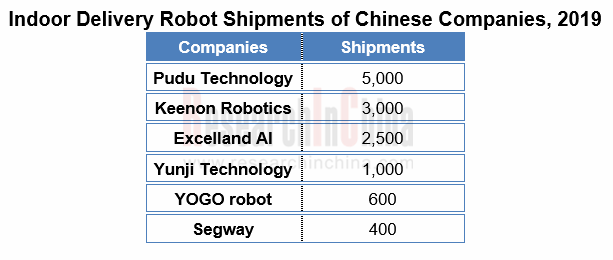
Comparatively, China stays ahead of foreign countries in the development of indoor delivery robots, where emerging players represented by Pudu Technology, Keenon Robotics, Excelland AI, YOGO, etc. have already offered basic products and been aggressively branching out into the multiple-scenario market alongside ceaseless iteration and speedy implementation of their technologies. In 2019, Pudu Technology shipped more than 5,000 units, Keenon Robotics 3,000 units, and other middle companies more than hundreds of units apiece.
Outdoor Autonomous Delivery Market
Against the huge market demand for instant delivery and express delivery as well as the decline in labor force in China, major companies are enthusiastically deploying autonomous delivery vehicles. Besides start-ups like Neolix, IdriverPlus and White Rhino, e-commerce and logistics companies such as JD.com, Meituan, Cainiao, Suning and China Post are also sparing no efforts in developing outdoor autonomous delivery business. Autonomous delivery vehicles are produced in small quantities in China and have not taken on a sizable scale yet, as is revealed by the companies concerned.
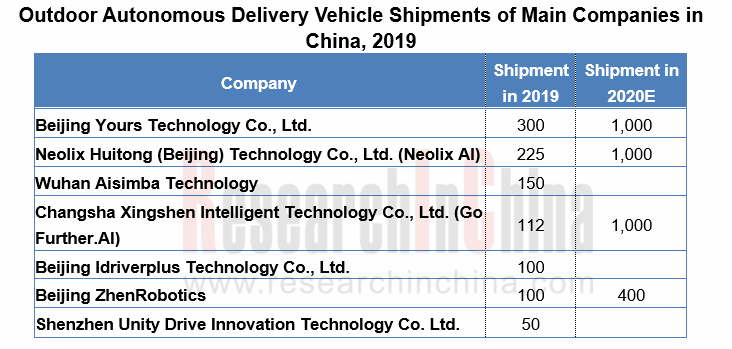
Constrained by imperfect policies and regulations, technology and scenario configurations, outdoor autonomous delivery vehicles are still undergoing pilot operation. Yet the industry gains momentum in 2020, with operations broadening from “single vehicle pilot run” to “closed scenarios/fixed route fleet operation”, and even to “city autonomous delivery operation”.
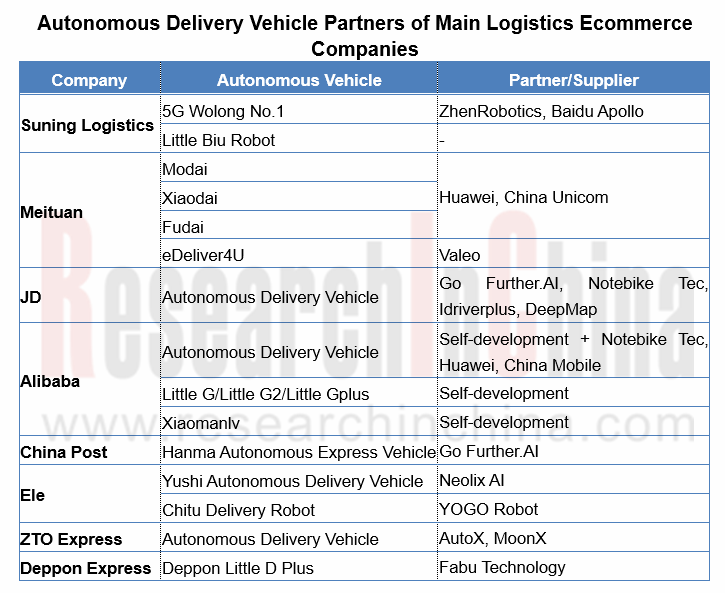
Ecommerce logistics companies thus deploy outdoor autonomous delivery vehicles in three ways: ① develop independently or partner with start-ups for deployment through logistics channels, for example, Alibaba self-develops Xiaomanlv autonomous robot and deploys it though Cainiao logistics distribution; ② work with governments, for example, Meituan and the People’s Government of Shunyi District, Beijing cooperated to deploy in the area; ③ joined hands with market players like retailors and supermarkets, for example, White Rhino Auto (Beijing) Technologies Co., Ltd. together with Yonghui Superstores introduced retail autonomous delivery.
Meituan’s autonomous delivery cars that came into service in Shunyi District of Beijing in early 2020, has been found in 15 communities of this district and surroundings and made delivery for a total of more than 10,000 orders for consecutive 270-plus days by the end of October, with support from the cooperative local government. These vehicles have become normal there. As concerns regulation, in September 2020, the People’s Government of Shunyi District, Beijing practiced a new approach to regulate: publicize the testing route and scheme of Meituan autonomous cars, allow them to run in designated places and in specific times, and define the one who is liable for safety. In its next step, Meituan plans to pilot low speed autonomous delivery on a larger scale together with Shunyi District by deploying 1,000 autonomous delivery vehicles that will run all day long throughout the area in the upcoming three years.
At APSARA Conference 2020 in September 2019, Alibaba’s first wheeled logistics robot called “Xiaomanlv” made a debut. Alibaba plans massive deployment of this vehicle in communities, schools and office parks. In October, Alibaba and Zijingang Campus of Zhejiang University built a fleet of 22 Xiaomanlv robots to deliver parcels from Cainiao logistics outlets to 27 dormitories. During the Singles' Day (2020.11.11) shopping festival, the fleet delivered 30,000 packages in all and saved 10,000 hours of pick-up time.
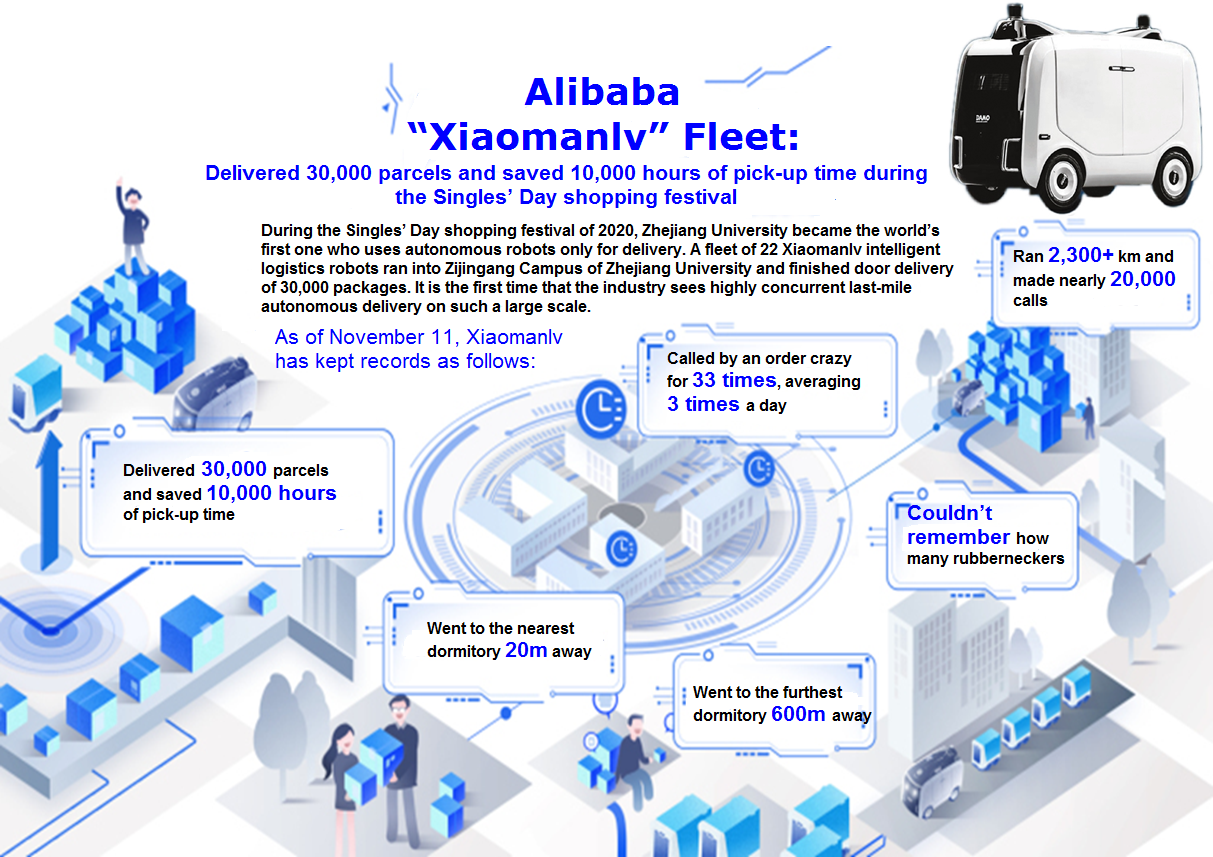
Alibaba “Xiaomanlv” Fleet
In October 2020, Jingdong Logistics (JDL) announced that it joined forces with Changshu City to construct the world’s first autonomous delivery city. JDL already deploys 5 models of 30-plus autonomous delivery vehicles available to different delivery scenarios in the downtown Changshu, and plans to put into use nearly 100 units before the end of the year. Also, JD has an “autonomous vehicle adoption” plan, that is, JDL’s couriers in the autonomous delivery area are allowed to apply for “adoption” of a set number of autonomous cars and act as the “commander” for the robot delivery task force, which means they can arrange the work for these members freely. A benign circle with links of technological innovation and service application thus takes shape to facilitate massive use of autonomous delivery vehicles and blaze a way for others to follow. JD also plans to bring at least 100,000 autonomous delivery robots into operation in the next five years.

JD Autonomous Delivery Robots Travelling on the Street of Changsha High-Tech Industrial Development Zone
In July 2018, Meituan announced to build an open autonomous delivery platform in an attempt to develop a complete autonomous delivery ecosystem in harness with governments, universities and companies. Meituan’s open autonomous delivery platform has joined hands with Nvidia (a chip vendor), Autox (an automated driving technology developer), Idriverplus, Yunji Technology (a commercial service robot developer) and Segway, as well as Chery, Valeo and other automakers and suppliers, and provides software and hardware integrated solutions together with them. In the meantime, Meituan’s partnerships with demanders using autonomous delivery vehicles in commercial scenarios, such as Joy City and China Fortune Land Development help to create a closed autonomous delivery ecosystem where demand and supply can benefit each other.
Autonomous Driving Domain Controller and Central Computing Unit (CCU) Industry Report, 2025
Research on Autonomous Driving Domain Controllers: Monthly Penetration Rate Exceeded 30% for the First Time, and 700T+ Ultrahigh-compute Domain Controller Products Are Rapidly Installed in Vehicles
L...
China Automotive Lighting and Ambient Lighting System Research Report, 2025
Automotive Lighting System Research: In 2025H1, Autonomous Driving System (ADS) Marker Lamps Saw an 11-Fold Year-on-Year Growth and the Installation Rate of Automotive LED Lighting Approached 90...
Ecological Domain and Automotive Hardware Expansion Research Report, 2025
ResearchInChina has released the Ecological Domain and Automotive Hardware Expansion Research Report, 2025, which delves into the application of various automotive extended hardware, supplier ecologic...
Automotive Seating Innovation Technology Trend Research Report, 2025
Automotive Seating Research: With Popularization of Comfort Functions, How to Properly "Stack Functions" for Seating?
This report studies the status quo of seating technologies and functions in aspe...
Research Report on Chinese Suppliers’ Overseas Layout of Intelligent Driving, 2025
Research on Overseas Layout of Intelligent Driving: There Are Multiple Challenges in Overseas Layout, and Light-Asset Cooperation with Foreign Suppliers Emerges as the Optimal Solution at Present
20...
High-Voltage Power Supply in New Energy Vehicle (BMS, BDU, Relay, Integrated Battery Box) Research Report, 2025
The high-voltage power supply system is a core component of new energy vehicles. The battery pack serves as the central energy source, with the capacity of power battery affecting the vehicle's range,...
Automotive Radio Frequency System-on-Chip (RF SoC) and Module Research Report, 2025
Automotive RF SoC Research: The Pace of Introducing "Nerve Endings" such as UWB, NTN Satellite Communication, NearLink, and WIFI into Intelligent Vehicles Quickens
RF SoC (Radio Frequency Syst...
Automotive Power Management ICs and Signal Chain Chips Industry Research Report, 2025
Analog chips are used to process continuous analog signals from the natural world, such as light, sound, electricity/magnetism, position/speed/acceleration, and temperature. They are mainly composed o...
Global and China Electronic Rearview Mirror Industry Report, 2025
Based on the installation location, electronic rearview mirrors can be divided into electronic interior rearview mirrors (i.e., streaming media rearview mirrors) and electronic exterior rearview mirro...
Intelligent Cockpit Tier 1 Supplier Research Report, 2025 (Chinese Companies)
Intelligent Cockpit Tier1 Suppliers Research: Emerging AI Cockpit Products Fuel Layout of Full-Scenario Cockpit Ecosystem
This report mainly analyzes the current layout, innovative products, and deve...
Next-generation Central and Zonal Communication Network Topology and Chip Industry Research Report, 2025
The automotive E/E architecture is evolving towards a "central computing + zonal control" architecture, where the central computing platform is responsible for high-computing-power tasks, and zonal co...
Vehicle-road-cloud Integration and C-V2X Industry Research Report, 2025
Vehicle-side C-V2X Application Scenarios: Transition from R16 to R17, Providing a Communication Base for High-level Autonomous Driving, with the C-V2X On-board Explosion Period Approaching
In 2024, t...
Intelligent Cockpit Patent Analysis Report, 2025
Patent Trend: Three Major Directions of Intelligent Cockpits in 2025
This report explores the development trends of cutting-edge intelligent cockpits from the perspective of patents. The research sco...
Smart Car Information Security (Cybersecurity and Data Security) Research Report, 2025
Research on Automotive Information Security: AI Fusion Intelligent Protection and Ecological Collaboration Ensure Cybersecurity and Data Security
At present, what are the security risks faced by inte...
New Energy Vehicle 800-1000V High-Voltage Architecture and Supply Chain Research Report, 2025
Research on 800-1000V Architecture: to be installed in over 7 million vehicles in 2030, marking the arrival of the era of full-domain high voltage and megawatt supercharging.
In 2025, the 800-1000V h...
Foreign Tier 1 ADAS Suppliers Industry Research Report 2025
Research on Overseas Tier 1 ADAS Suppliers: Three Paths for Foreign Enterprises to Transfer to NOA
Foreign Tier 1 ADAS suppliers are obviously lagging behind in the field of NOA.
In 2024, Aptiv (2.6...
VLA Large Model Applications in Automotive and Robotics Research Report, 2025
ResearchInChina releases "VLA Large Model Applications in Automotive and Robotics Research Report, 2025": The report summarizes and analyzes the technical origin, development stages, application cases...
OEMs’ Next-generation In-vehicle Infotainment (IVI) System Trends Report, 2025
ResearchInChina releases the "OEMs’ Next-generation In-vehicle Infotainment (IVI) System Trends Report, 2025", which sorts out iterative development context of mainstream automakers in terms of infota...