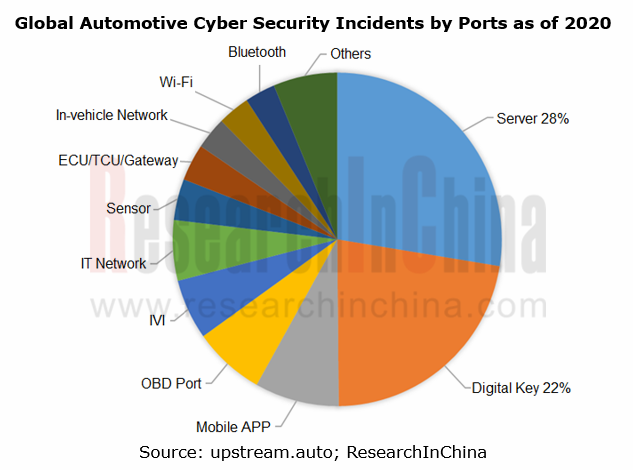
Research into automotive cyber security: server and digital key are the ports vulnerable to attacks, for which OEMs have stepped up efforts in cyber security.
With advances in the CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Electrified) trend, cars are going smarter ever with functional enrichment. Statistically, the installation rate of telematics feature to new cars in China is over 50% from January to October of 2020, a figure projected to rise to 75% or so in 2025. In terms of functionality, intelligent cockpit and advanced automated driving become trending, and the features such as multi-modal interaction, multi-display interaction, 5G connectivity, V2X, OTA and digital key finds ever broader application alongside the soaring number of vehicle control codes and more port vulnerabilities to safety threat.
Currently, the automotive cyber security events arise mainly from attacks on server, digital key, mobile APP, OBD port among others.
Server acts as the most important port for cyber security, which is exposed to the attack by hackers on operating system, database, TSP server, OTA server and the like, thus issuing in data tampering, damage and vehicle safety accidents. Most tools of assault on servers are remotely accessible with lower costs, while the data storage over servers is of paramount importance, all of which lead to often a rather high share of attacks on servers.
Digital key, as the second port that matters most to cyber security, is a common media subject to vehicle intrusion and theft. In 2020, there will be 300,000 Bluetooth digital key installs in China, coupled with an installation rate at about 4%, with such more functionalities besides lock/unlock & start as account log-in, key sharing, vehicle trajectory record, and parcel delivery to cars, which has ever more implications on vehicle safety.
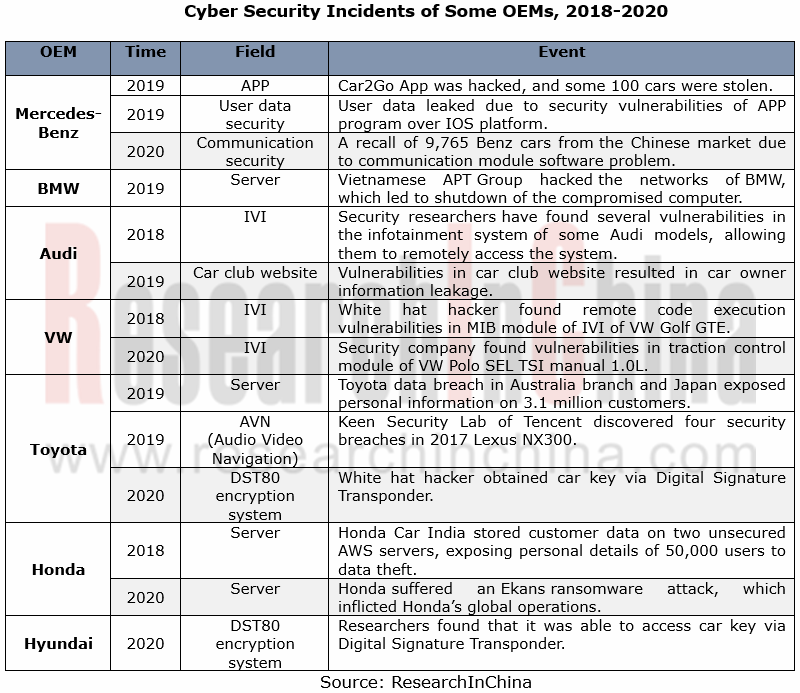
Different auto brands are subject to varied attack on vehicle security.
The smarter a car is, the more vulnerable to security attacks will be. Amid the intelligence trend, all OEMs, whatever Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Audi, VW, Toyota, Honda or Hyundai, have varied exposure to security attacks.
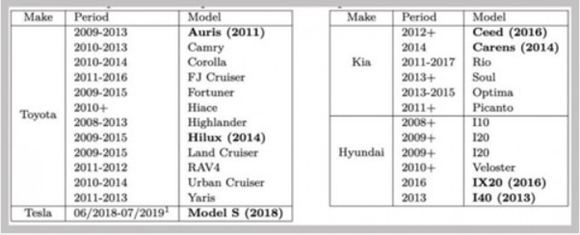
In March 2020, key encryption approaches of OEMs like Toyota, Hyundai and KIA were reported to have limitations with a possibility of intrusions and thefts largely due to the vulnerabilities of TI’s DST80 encryption system employed by them. A hacker just stands near the car that packs DST80 remote control key, using the inexpensive Proxmark RFID reader/transmitter for the ‘identity theft’ of the key and thus getting the encrypted information.
OEM quicken their presence in cyber security
To address serious challenges in automotive cyber security, the OEMs are sparing no efforts in security improvement in many aspects: a) information management inside the company and optimization of R&D process; 2) to build a team intended for cyber security; 3) cyber security protection of telematics.
> European and American OEMs: Diversified deployments of cyber security protection
The automakers from Europe and America are pushing ahead with cyber security construction roundly with technical superiorities, with a tightened control on information security management inside the company apart from improvements in cyber security protection of telematics. As concerns team construction, the majority of European and American OEMs as usual set up either an independent cyber security division or a subsidiary to ensure information security during a vehicle lifespan.
Mercedes-Benz, for instance, has such actions for cyber security in the three below:
Cloud computing: vehicle data protection enabled by a cloud platform through which the car owner takes control of data openness to the outside while driving, and at the same time relevant information will be eliminated automatically after the car owner leaves his/her car;
Factory: partnership with telecom carriers and equipment vendors to set up intelligent vehicle manufacturing factories with production data safety enabled by 5G mobile network;
Vulnerability protection: joins forces with third-party cybersecurity providers to test and repair the potential vulnerabilities of intelligent connected vehicle.
> Japanese and Korean OEMs: with a more focus on cyber security protection and management inside the company
Nissan Motor, for example, proceeds with intro-company management on information security and perfects the regulations concerned. Over the recent years, Nissan has been improving its R&D management system and cyber security platform, with its Tel Aviv-based joint innovation laboratory and collaborations with Israeli start-ups on cyber security testing and study. As yet, Nissan has more than ten cooperative joint prototype projects.
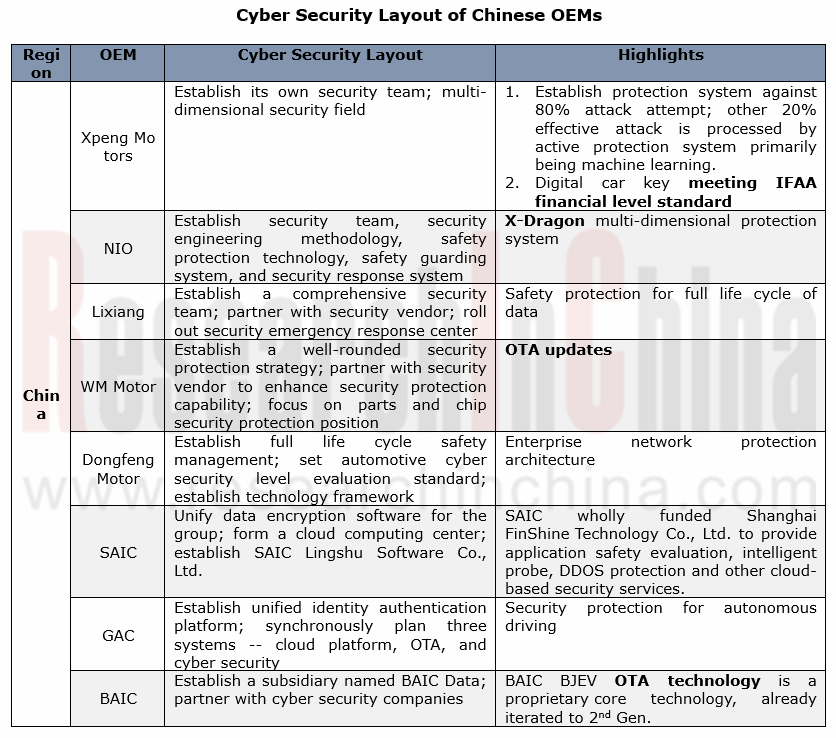
> Chinese OEMs: the emerging forces go ahead of the rest
The emerging carmakers are commendable in cyber security protection. Cases include XPENG Motors that boast concurrent deployments over cloud, vehicle and mobile phone by building a security team on its own and the partnerships with Aliyun, Irdeto, and Keen Security Lab of Tencent in order for a proactive protection system; and NIO that has built a X-Dragon multi-dimensional protection system through a self-owned security team and multi-party cooperation.
Also, the time-honored Chinese automakers follow suit, such as Dongfeng Motor, SAIC, GAC and BAIC that all prioritize the security stewardship during their life cycle. As concerns its overall deployment, SAIC, for example, incorporates its subordinates into the group’s cyber security protection and management system and applies the data encryption software (GS-EDS system) with one accord for data safety as a whole; secondly, SAIC builds a cloud platform independently and a proprietary cloud computing center delivering cloud-based security services; last, SAIC founded SAIC Lingshu Software Co., Ltd in charge of developing basic technology platform and sharpening software R&D competence.
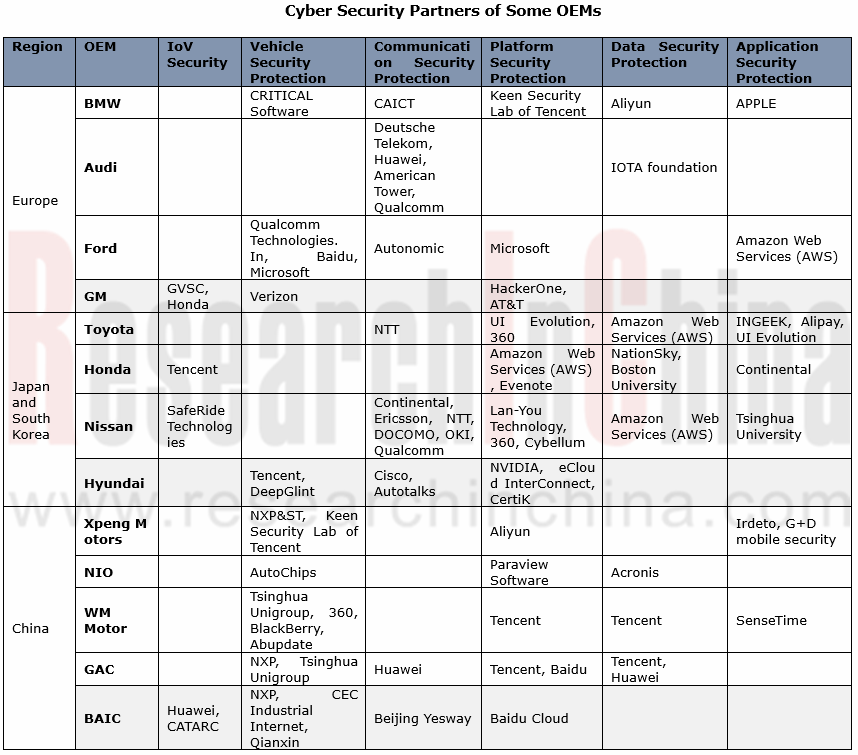
OEMs have ever broader cooperation in cyber security.
In addition to security enhancement, OEMs are vigorously seeking for external collaborations on vehicle, communication, platform, data, and application, to name a few.
Autonomous Driving Domain Controller and Central Computing Unit (CCU) Industry Report, 2025
Research on Autonomous Driving Domain Controllers: Monthly Penetration Rate Exceeded 30% for the First Time, and 700T+ Ultrahigh-compute Domain Controller Products Are Rapidly Installed in Vehicles
L...
China Automotive Lighting and Ambient Lighting System Research Report, 2025
Automotive Lighting System Research: In 2025H1, Autonomous Driving System (ADS) Marker Lamps Saw an 11-Fold Year-on-Year Growth and the Installation Rate of Automotive LED Lighting Approached 90...
Ecological Domain and Automotive Hardware Expansion Research Report, 2025
ResearchInChina has released the Ecological Domain and Automotive Hardware Expansion Research Report, 2025, which delves into the application of various automotive extended hardware, supplier ecologic...
Automotive Seating Innovation Technology Trend Research Report, 2025
Automotive Seating Research: With Popularization of Comfort Functions, How to Properly "Stack Functions" for Seating?
This report studies the status quo of seating technologies and functions in aspe...
Research Report on Chinese Suppliers’ Overseas Layout of Intelligent Driving, 2025
Research on Overseas Layout of Intelligent Driving: There Are Multiple Challenges in Overseas Layout, and Light-Asset Cooperation with Foreign Suppliers Emerges as the Optimal Solution at Present
20...
High-Voltage Power Supply in New Energy Vehicle (BMS, BDU, Relay, Integrated Battery Box) Research Report, 2025
The high-voltage power supply system is a core component of new energy vehicles. The battery pack serves as the central energy source, with the capacity of power battery affecting the vehicle's range,...
Automotive Radio Frequency System-on-Chip (RF SoC) and Module Research Report, 2025
Automotive RF SoC Research: The Pace of Introducing "Nerve Endings" such as UWB, NTN Satellite Communication, NearLink, and WIFI into Intelligent Vehicles Quickens
RF SoC (Radio Frequency Syst...
Automotive Power Management ICs and Signal Chain Chips Industry Research Report, 2025
Analog chips are used to process continuous analog signals from the natural world, such as light, sound, electricity/magnetism, position/speed/acceleration, and temperature. They are mainly composed o...
Global and China Electronic Rearview Mirror Industry Report, 2025
Based on the installation location, electronic rearview mirrors can be divided into electronic interior rearview mirrors (i.e., streaming media rearview mirrors) and electronic exterior rearview mirro...
Intelligent Cockpit Tier 1 Supplier Research Report, 2025 (Chinese Companies)
Intelligent Cockpit Tier1 Suppliers Research: Emerging AI Cockpit Products Fuel Layout of Full-Scenario Cockpit Ecosystem
This report mainly analyzes the current layout, innovative products, and deve...
Next-generation Central and Zonal Communication Network Topology and Chip Industry Research Report, 2025
The automotive E/E architecture is evolving towards a "central computing + zonal control" architecture, where the central computing platform is responsible for high-computing-power tasks, and zonal co...
Vehicle-road-cloud Integration and C-V2X Industry Research Report, 2025
Vehicle-side C-V2X Application Scenarios: Transition from R16 to R17, Providing a Communication Base for High-level Autonomous Driving, with the C-V2X On-board Explosion Period Approaching
In 2024, t...
Intelligent Cockpit Patent Analysis Report, 2025
Patent Trend: Three Major Directions of Intelligent Cockpits in 2025
This report explores the development trends of cutting-edge intelligent cockpits from the perspective of patents. The research sco...
Smart Car Information Security (Cybersecurity and Data Security) Research Report, 2025
Research on Automotive Information Security: AI Fusion Intelligent Protection and Ecological Collaboration Ensure Cybersecurity and Data Security
At present, what are the security risks faced by inte...
New Energy Vehicle 800-1000V High-Voltage Architecture and Supply Chain Research Report, 2025
Research on 800-1000V Architecture: to be installed in over 7 million vehicles in 2030, marking the arrival of the era of full-domain high voltage and megawatt supercharging.
In 2025, the 800-1000V h...
Foreign Tier 1 ADAS Suppliers Industry Research Report 2025
Research on Overseas Tier 1 ADAS Suppliers: Three Paths for Foreign Enterprises to Transfer to NOA
Foreign Tier 1 ADAS suppliers are obviously lagging behind in the field of NOA.
In 2024, Aptiv (2.6...
VLA Large Model Applications in Automotive and Robotics Research Report, 2025
ResearchInChina releases "VLA Large Model Applications in Automotive and Robotics Research Report, 2025": The report summarizes and analyzes the technical origin, development stages, application cases...
OEMs’ Next-generation In-vehicle Infotainment (IVI) System Trends Report, 2025
ResearchInChina releases the "OEMs’ Next-generation In-vehicle Infotainment (IVI) System Trends Report, 2025", which sorts out iterative development context of mainstream automakers in terms of infota...