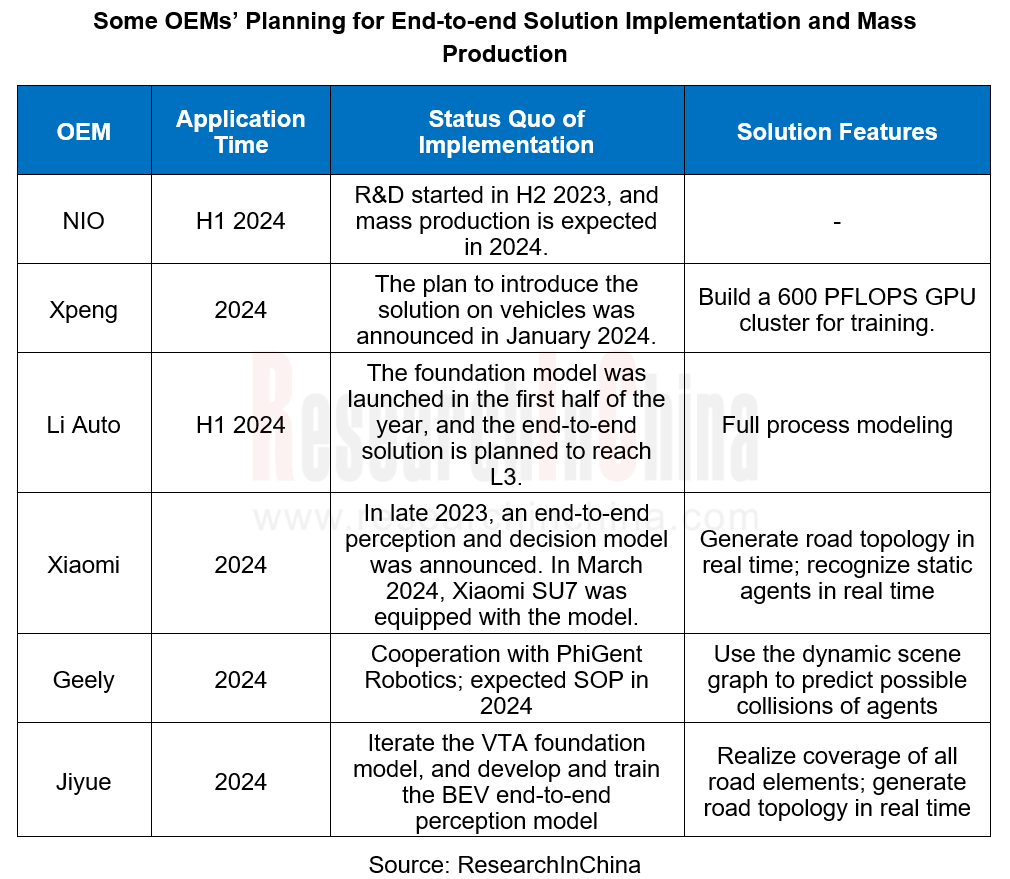
End-to-end Autonomous Driving Research: status quo of End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving
1. Status quo of end-to-end solutions in China
An end-to-end autonomous driving system refers to direct mapping from sensor data inputs (camera images, LiDAR, etc.) to control command outputs (steering, acceleration/deceleration, etc.). It first appeared in the ALVINN project in 1988. It uses cameras and laser rangefinders as input and a simple neural network to generate steering as output.
In early 2024, Tesla rolled out FSD V12.3, featuring an amazing intelligent driving level. The end-to-end autonomous driving solution garners widespread attention from OEMs and autonomous driving solution companies in China.?
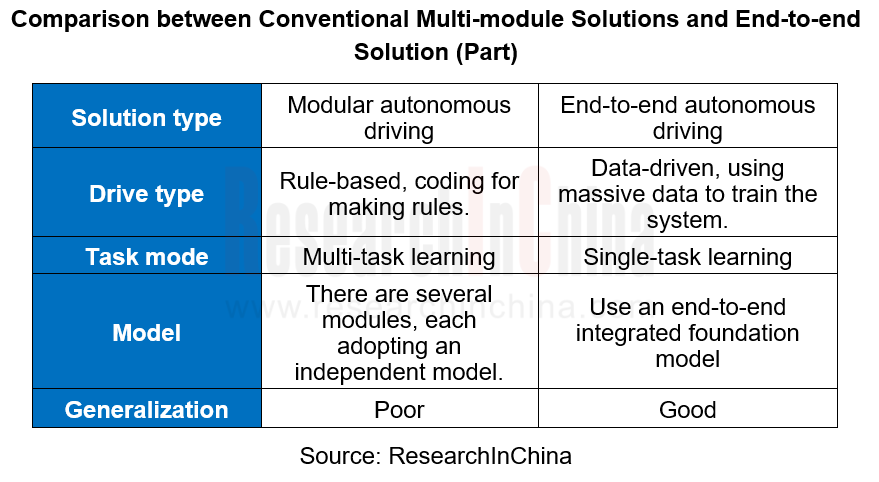
Compared with conventional multi-module solutions, the end-to-end autonomous driving solution integrates perception, prediction and planning into a single model, simplifying the solution structure. It can simulate human drivers making driving decisions directly according to visual inputs, effectively cope with long tail scenarios of modular solutions and improve the training efficiency and performance of models.

Li Auto's end-to-end solution
Li Auto believes that a complete end-to-end model should cover the whole process of perception, tracking, prediction, decision and planning, and it is the optimal solution to achieve L3 autonomous driving. In 2023, Li Auto pushed AD Max3.0, with overall framework reflecting the end-to-end concept but still a gap with a complete end-to-end solution. In 2024, Li Auto is expected to promote the system to become a complete end-to-end solution.?
Li Auto's autonomous driving framework is shown below, consisting of two systems:
Fast system: System 1, Li Auto’s existing end-to-end solution which is directly executed after perceiving the surroundings.
Slow system: System 2, a multimodal large language model that logically thinks and explores unknown environments to solve problems in unknown L4 scenarios.
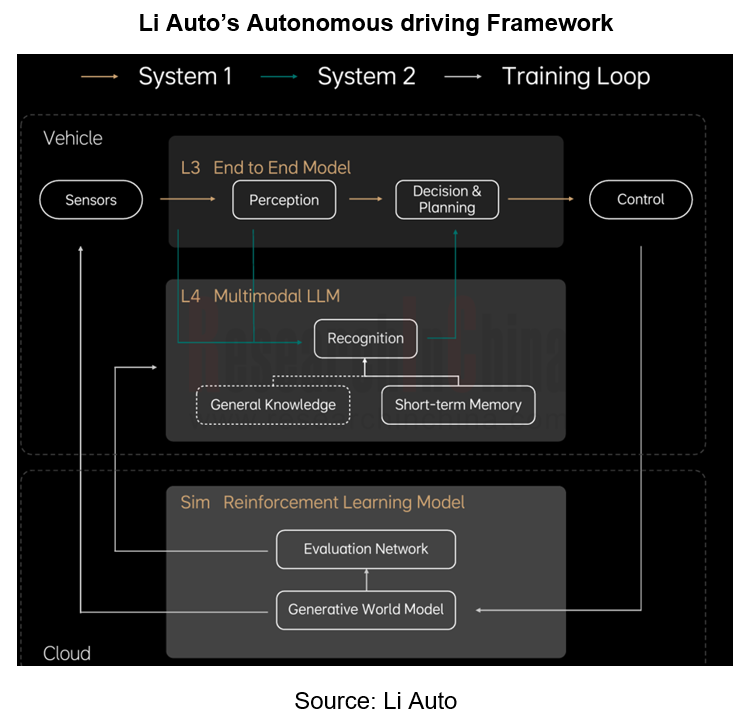
In the process of promoting the end-to-end solution, Li Auto plans to unify the planning/forecast model and the perception model, and accomplish the end-to-end Temporal Planner on the original basis to integrate parking with driving.
2. Data becomes the key to the implementation of end-to-end solutions.
The implementation of an end-to-end solution requires processes covering R&D team building, hardware facilities, data collection and processing, algorithm training and strategy customization, verification and evaluation, promotion and mass production. Some of the sore points in scenarios are as shown in the table:
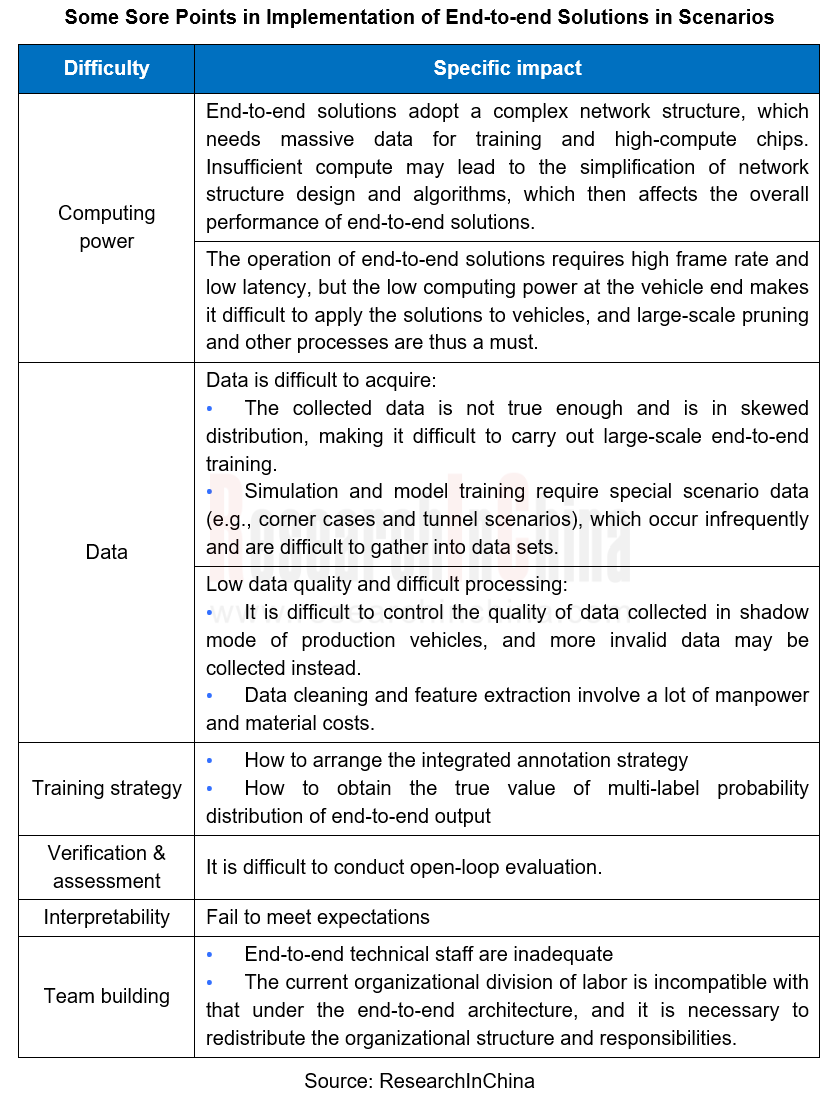
The integrated training in end-to-end autonomous driving solutions requires massive data, so one of the difficulties it faces lies in data collection and processing.
First of all, it needs a long time and may channels to collect data, including driving data and scenario data such as roads, weather and traffic conditions. In actual driving, the data within the driver's front view is relatively easy to collect, but the surrounding information is hard to say.
During data processing, it is necessary to design data extraction dimensions, extract effective features from massive video clips, make statistics of data distribution, etc. to support large-scale data training.
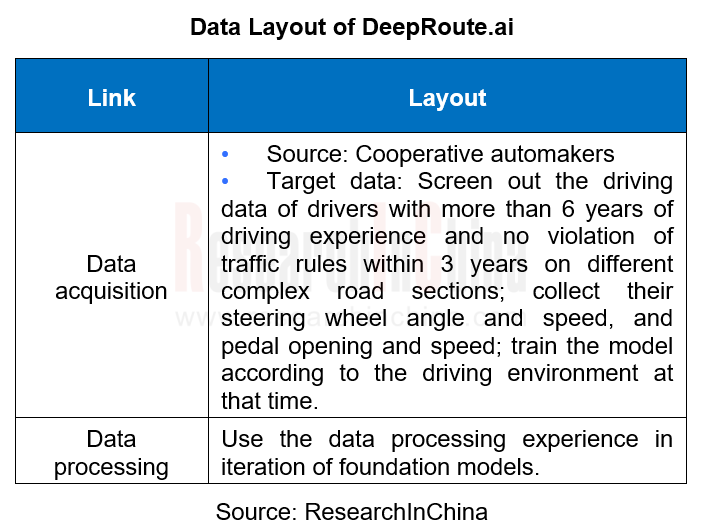
DeepRoute
As of March 2024, DeepRoute.ai's end-to-end autonomous driving solution has been designated by Great Wall Motor and involved in the cooperation with NVIDIA. It is expected to adapt to NVIDIA Thor in 2025. In the planning of DeepRoute.ai, the transition from the conventional solution to the "end-to-end" autonomous driving solution will go through sensor pre-fusion, HD map removal, and integration of perception, decision and control.
GigaStudio
DriveDreamer, an autonomous driving model of GigaStudio, is capable of scenario generation, data generation, driving action prediction and so forth. In the scenario/data generation, it has two steps:
When involving single-frame structural conditions, guide DriveDreamer to generate driving scenario images, so that it can understand structural traffic constraints easily.
Extend its understanding to video generation. Using continuous traffic structure conditions, DriveDreamer outputs driving scene videos to further enhance its understanding of motion transformation.

3. End-to-end solutions accelerate the application of embodied robots.
In addition to autonomous vehicles, embodied robots are another mainstream scenario of end-to-end solutions. From end-to-end autonomous driving to robots, it is necessary to build a more universal world model to adapt to more complex and diverse real application scenarios. The development framework of mainstream AGI (General Artificial Intelligence) is divided into two stages:
Stage 1: the understanding and generation of basic foundation models are unified, and further combined with embodied artificial intelligence (embodied AI) to form a unified world model;
Stage 2: capabilities of world model + complex task planning and control, and abstract concept induction gradually evolve into the era of the interactive AGI 1.0.
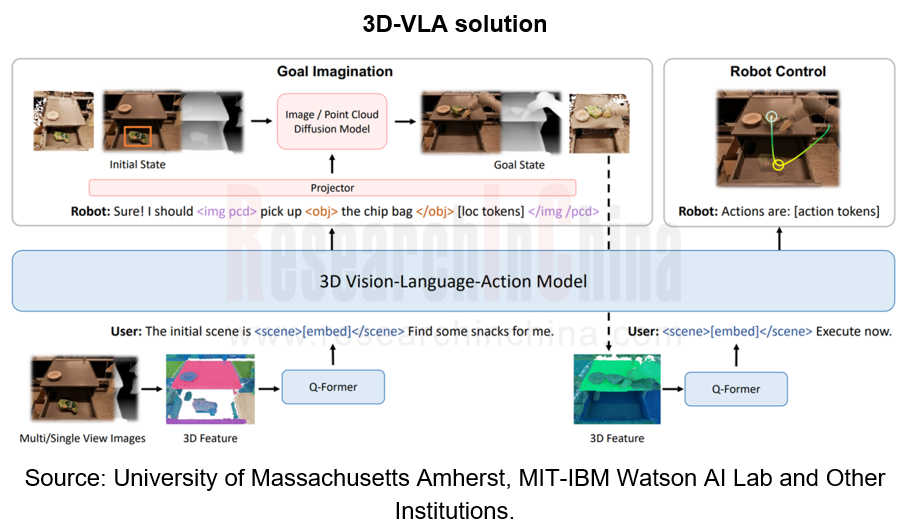
In the landing process of the world model, the construction of an end-to-end VLA (Vision-Language-Action) autonomous system has become a crucial link. VLA, as the basic foundation model of embodied AI, can seamlessly link 3D perception, reasoning and action to form a generative world model, which is built on the 3D-based large language model (LLM) and introduces a set of interactive markers to interact with the environment.
As of April 2024, some manufacturers of humanoid robots adopting end-to-end solutions are as follows:
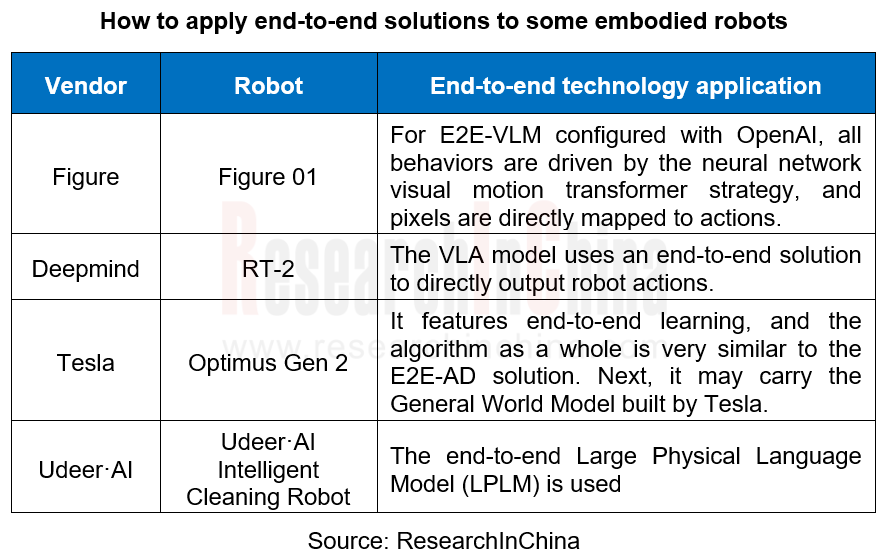
For example, Udeer·AI's Large Physical Language Model (LPLM) is an end-to-end embodied AI solution that uses a self-labeling mechanism to improve the learning efficiency and quality of the model from unlabeled data, thereby deepening the understanding of the world and enhancing the robot's generalization capabilities and environmental adaptability in cross-modal, cross-scene, and cross-industry scenarios.
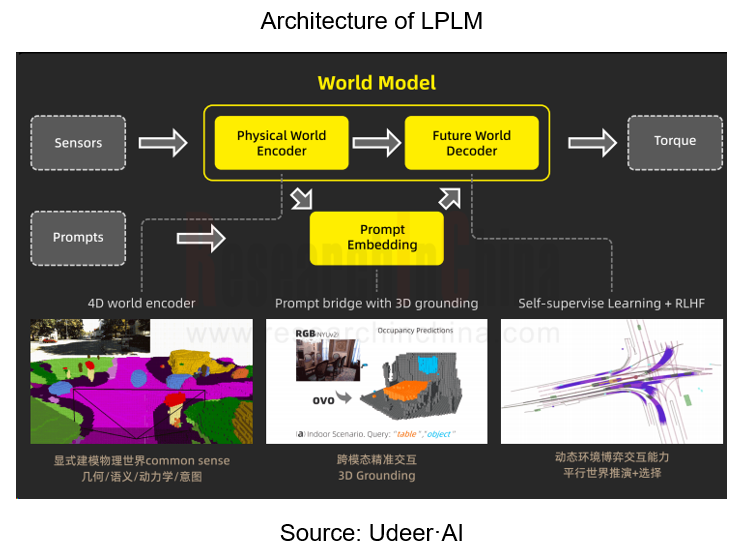
LPLM abstracts the physical world and ensures that this kind of information is aligned with the abstract level of features in LLM. It explicitly models each entity in the physical world as a token, and encodes geometric, semantic, kinematic and intentional information.
In addition, LPLM adds 3D grounding to the encoding of natural language instructions, improving the accuracy of natural language to some extent. Its decoder can learn by constantly predicting the future, thus strengthening the ability of the model to learn from massive unlabeled data.
End-to-End Autonomous Driving Research Report, 2025
End-to-End Autonomous Driving Research: E2E Evolution towards the VLA Paradigm via Synergy of Reinforcement Learning and World Models??The essence of end-to-end autonomous driving lies in mimicking dr...
Research Report on OEMs and Tier1s’ Intelligent Cockpit Platforms (Hardware & Software) and Supply Chain Construction Strategies, 2025
Research on intelligent cockpit platforms: in the first year of mass production of L3 AI cockpits, the supply chain accelerates deployment of new products
An intelligent cockpit platform primarily r...
Automotive EMS and ECU Industry Report, 2025
Research on automotive EMS: Analysis on the incremental logic of more than 40 types of automotive ECUs and EMS market segments
In this report, we divide automotive ECUs into five major categories (in...
Automotive Intelligent Cockpit SoC Research Report, 2025
Cockpit SoC research: The localization rate exceeds 10%, and AI-oriented cockpit SoC will become the mainstream in the next 2-3 years
In the Chinese automotive intelligent cockpit SoC market, althoug...
Auto Shanghai 2025 Summary Report
The post-show summary report of 2025 Shanghai Auto Show, which mainly includes three parts: the exhibition introduction, OEM, and suppliers. Among them, OEM includes the introduction of models a...
Automotive Operating System and AIOS Integration Research Report, 2025
Research on automotive AI operating system (AIOS): from AI application and AI-driven to AI-native
Automotive Operating System and AIOS Integration Research Report, 2025, released by ResearchInChina, ...
Software-Defined Vehicles in 2025: OEM Software Development and Supply Chain Deployment Strategy Research Report
SDV Research: OEM software development and supply chain deployment strategies from 48 dimensions
The overall framework of software-defined vehicles: (1) Application software layer: cockpit software, ...
Research Report on Automotive Memory Chip Industry and Its Impact on Foundation Models, 2025
Research on automotive memory chips: driven by foundation models, performance requirements and costs of automotive memory chips are greatly improved.
From 2D+CNN small models to BEV+Transformer found...
48V Low-voltage Power Distribution Network (PDN) Architecture and Supply Chain Panorama Research Report, 2025
For a long time, the 48V low-voltage PDN architecture has been dominated by 48V mild hybrids. The electrical topology of 48V mild hybrids is relatively outdated, and Chinese OEMs have not given it suf...
Research Report on Overseas Cockpit Configuration and Supply Chain of Key Models, 2025
Overseas Cockpit Research: Tariffs stir up the global automotive market, and intelligent cockpits promote automobile exports
ResearchInChina has released the Research Report on Overseas Cockpit Co...
Automotive Display, Center Console and Cluster Industry Report, 2025
In addition to cockpit interaction, automotive display is another important carrier of the intelligent cockpit. In recent years, the intelligence level of cockpits has continued to improve, and automo...
Vehicle Functional Safety and Safety Of The Intended Functionality (SOTIF) Research Report, 2025
Functional safety research: under the "equal rights for intelligent driving", safety of the intended functionality (SOTIF) design is crucial
As Chinese new energy vehicle manufacturers propose "Equal...
Chinese OEMs’ AI-Defined Vehicle Strategy Research Report, 2025
AI-Defined Vehicle Report: How AI Reshapes Vehicle Intelligence?
Chinese OEMs’ AI-Defined Vehicle Strategy Research Report, 2025, released by ResearchInChina, studies, analyzes, and summarizes the c...
Automotive Digital Key (UWB, NearLink, and BLE 6.0) Industry Trend Report, 2025
Digital key research: which will dominate digital keys, growing UWB, emerging NearLink or promising Bluetooth 6.0?ResearchInChina has analyzed and predicted the digital key market, communication techn...
Integrated Battery (CTP, CTB, CTC, and CTV) and Battery Innovation Technology Report, 2025
Power battery research: 17 vehicle models use integrated batteries, and 34 battery innovation technologies are released
ResearchInChina released Integrated Battery (CTP, CTB, CTC, and CTV)and Battery...
AI/AR Glasses Industry Research Report, 2025
ResearchInChina released the " AI/AR Glasses Industry Research Report, 2025", which deeply explores the field of AI smart glasses, sorts out product R&D and ecological layout of leading domestic a...
Global and China Passenger Car T-Box Market Report 2025
T-Box Research: T-Box will achieve functional upgrades given the demand from CVIS and end-to-end autonomous driving
ResearchInChina released the "Global and China Passenger Car T-Box Market Report 20...
Automotive Microcontroller Unit (MCU) Industry Report, 2025
Research on automotive MCUs: the independent, controllable supply chain for automotive MCUs is rapidly maturing
Mid-to-high-end MCUs for intelligent vehicle control are a key focus of domestic produc...