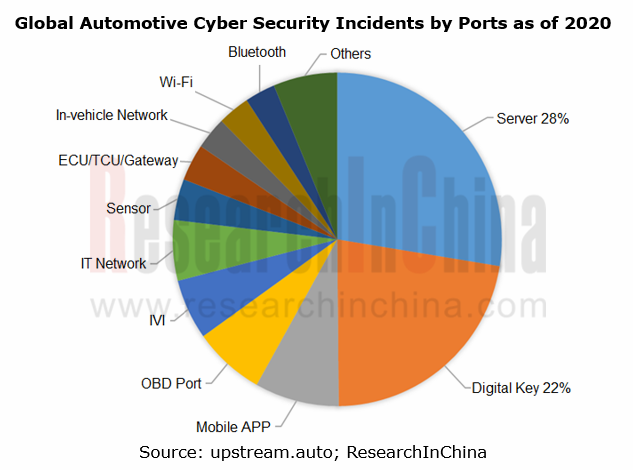
Research into automotive cyber security: server and digital key are the ports vulnerable to attacks, for which OEMs have stepped up efforts in cyber security.
With advances in the CASE (Connected, Autonomous, Shared, and Electrified) trend, cars are going smarter ever with functional enrichment. Statistically, the installation rate of telematics feature to new cars in China is over 50% from January to October of 2020, a figure projected to rise to 75% or so in 2025. In terms of functionality, intelligent cockpit and advanced automated driving become trending, and the features such as multi-modal interaction, multi-display interaction, 5G connectivity, V2X, OTA and digital key finds ever broader application alongside the soaring number of vehicle control codes and more port vulnerabilities to safety threat.
Currently, the automotive cyber security events arise mainly from attacks on server, digital key, mobile APP, OBD port among others.
Server acts as the most important port for cyber security, which is exposed to the attack by hackers on operating system, database, TSP server, OTA server and the like, thus issuing in data tampering, damage and vehicle safety accidents. Most tools of assault on servers are remotely accessible with lower costs, while the data storage over servers is of paramount importance, all of which lead to often a rather high share of attacks on servers.
Digital key, as the second port that matters most to cyber security, is a common media subject to vehicle intrusion and theft. In 2020, there will be 300,000 Bluetooth digital key installs in China, coupled with an installation rate at about 4%, with such more functionalities besides lock/unlock & start as account log-in, key sharing, vehicle trajectory record, and parcel delivery to cars, which has ever more implications on vehicle safety.
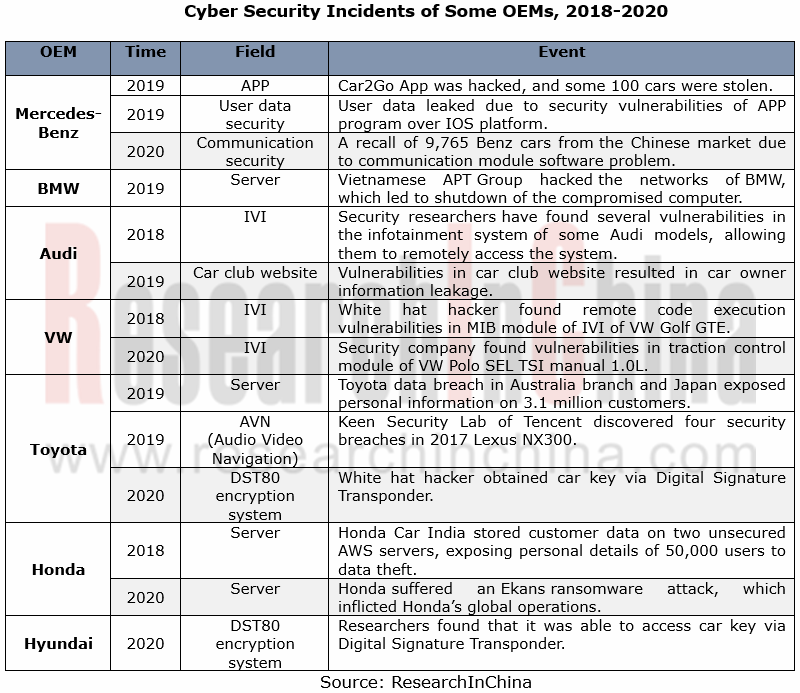
Different auto brands are subject to varied attack on vehicle security.
The smarter a car is, the more vulnerable to security attacks will be. Amid the intelligence trend, all OEMs, whatever Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Audi, VW, Toyota, Honda or Hyundai, have varied exposure to security attacks.
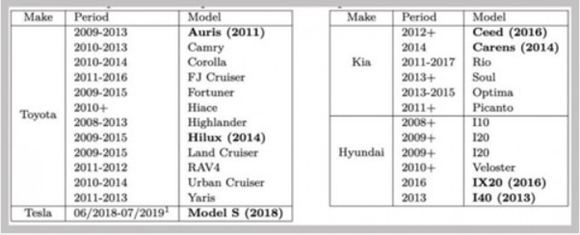
In March 2020, key encryption approaches of OEMs like Toyota, Hyundai and KIA were reported to have limitations with a possibility of intrusions and thefts largely due to the vulnerabilities of TI’s DST80 encryption system employed by them. A hacker just stands near the car that packs DST80 remote control key, using the inexpensive Proxmark RFID reader/transmitter for the ‘identity theft’ of the key and thus getting the encrypted information.
OEM quicken their presence in cyber security
To address serious challenges in automotive cyber security, the OEMs are sparing no efforts in security improvement in many aspects: a) information management inside the company and optimization of R&D process; 2) to build a team intended for cyber security; 3) cyber security protection of telematics.
> European and American OEMs: Diversified deployments of cyber security protection
The automakers from Europe and America are pushing ahead with cyber security construction roundly with technical superiorities, with a tightened control on information security management inside the company apart from improvements in cyber security protection of telematics. As concerns team construction, the majority of European and American OEMs as usual set up either an independent cyber security division or a subsidiary to ensure information security during a vehicle lifespan.
Mercedes-Benz, for instance, has such actions for cyber security in the three below:
Cloud computing: vehicle data protection enabled by a cloud platform through which the car owner takes control of data openness to the outside while driving, and at the same time relevant information will be eliminated automatically after the car owner leaves his/her car;
Factory: partnership with telecom carriers and equipment vendors to set up intelligent vehicle manufacturing factories with production data safety enabled by 5G mobile network;
Vulnerability protection: joins forces with third-party cybersecurity providers to test and repair the potential vulnerabilities of intelligent connected vehicle.
> Japanese and Korean OEMs: with a more focus on cyber security protection and management inside the company
Nissan Motor, for example, proceeds with intro-company management on information security and perfects the regulations concerned. Over the recent years, Nissan has been improving its R&D management system and cyber security platform, with its Tel Aviv-based joint innovation laboratory and collaborations with Israeli start-ups on cyber security testing and study. As yet, Nissan has more than ten cooperative joint prototype projects.
> Chinese OEMs: the emerging forces go ahead of the rest
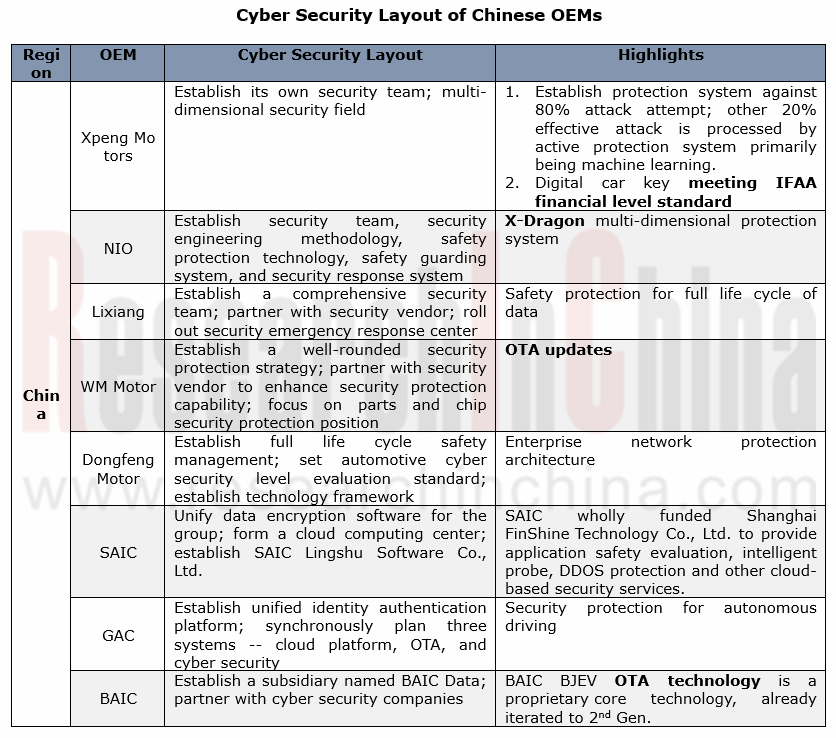
The emerging carmakers are commendable in cyber security protection. Cases include XPENG Motors that boast concurrent deployments over cloud, vehicle and mobile phone by building a security team on its own and the partnerships with Aliyun, Irdeto, and Keen Security Lab of Tencent in order for a proactive protection system; and NIO that has built a X-Dragon multi-dimensional protection system through a self-owned security team and multi-party cooperation.
Also, the time-honored Chinese automakers follow suit, such as Dongfeng Motor, SAIC, GAC and BAIC that all prioritize the security stewardship during their life cycle. As concerns its overall deployment, SAIC, for example, incorporates its subordinates into the group’s cyber security protection and management system and applies the data encryption software (GS-EDS system) with one accord for data safety as a whole; secondly, SAIC builds a cloud platform independently and a proprietary cloud computing center delivering cloud-based security services; last, SAIC founded SAIC Lingshu Software Co., Ltd in charge of developing basic technology platform and sharpening software R&D competence.
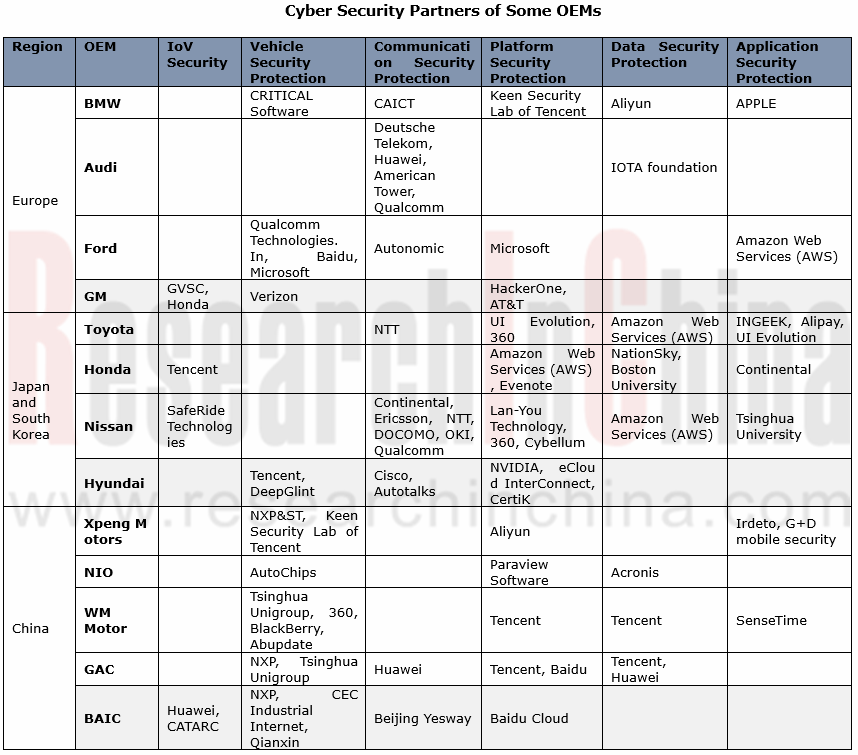
OEMs have ever broader cooperation in cyber security.
In addition to security enhancement, OEMs are vigorously seeking for external collaborations on vehicle, communication, platform, data, and application, to name a few.
Global and China Leading Tier1 Suppliers’ Intelligent Cockpit Business Research Report, 2022 (II)
Tier1 Intelligent Cockpit Research: The mass production of innovative cockpits gathers pace, and penetration of new technologies is on a rapid riseGlobal OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers are racing for the i...
Global and China Leading Tier1 Suppliers’ Intelligent Cockpit Business Research Report, 2022 (I)
Tier1 Intelligent Cockpit Research: The mass production of innovative cockpits gathers pace, and penetration of new technologies is on a rapid riseGlobal OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers are racing for the i...
China Commercial Vehicle Intelligent Cockpit Industry Report 2021
Research on Intelligent Cockpits of Commercial Vehicles: Heading for Large Screens, Voice Interaction, Entertainment and Life
Following AD/ADAS functions, the intelligent configuration of the cockpit...
Automotive Ultra Wide Band (UWB) Industry Report, 2022
UWB got initially utilized in the military field, and began to be commercially applied after the release of criteria for UWB commercialization in 2002. In 2019, Car Connectivity Consortium (CCC) liste...
China Automotive Distribution and Aftermarket Industry Report, 2022-2027
Since the introduction of 4S store model into China at the end of 20th century, China's authorized dealer system has gradually developed from a single-store-based mode to a group-based mode, and from ...
Global and China Skateboard Chassis Industry Report, 2021-2022
Research into skateboard chassis: where to sell, how to sell and to whom it is sold
Rivian, a new carmaker based on skateboard chassis, is quite popular in the market and becomes the focus of the aut...
Emerging Automakers Strategy Research Report, 2022--NIO
Research on emerging carmaking strategies: no new cars in 2021, 3 new cars in 2022, can NIO make its renaissance?
The delivery of ET7 is imminent, and the sluggish sales situation is expected to fade...
Automotive and 5G Industry Integration Development Report, 2022
Research on integration of vehicle and 5G: OEMs rush into mass production of 5G models whose sales may reach 3.68 million units in 2025
By the end of 2021, China had built and opened in excess of 1.3...
China Automotive Finance Industry Report, 2022-2030
Auto finance is lucrative with the highest profit margin in the international automobile industry chain, contributing to roughly 23% of the global automobile industry profits. Yet, auto finance only h...
Global and China Power Battery Management System (BMS) Industry Report, 2022-2026
1. Robust demand from new energy vehicle spurs BMS market to boom
New energy vehicle sales have been growing rapidly worldwide over the recent years, reaching 6.5 million units with a year-on-year up...
ADAS/AD Chip Industry Research Report, 2022
Autonomous driving chip research: In addition to computing power, core IP, software stacks, AI training platforms, etc. are becoming more and more importantL2.5 and L2.9 have achieved mass production ...
Automotive Sensor Chip Industry Research Report, 2022
Sensor Chip Research: Automotive Sensors Have Entered a Technology Iteration Cycle, and Opportunities for Localization of Chips Are Coming Automotive sensor chips can obtain external environment ...
Automotive Cloud Service Platform Industry Report, 2021-2022
Research on Automotive Cloud Services: Based on 5ABCD, cloud services run through the R&D, production, sale, management and services of automakersWith the development of intelligent connectivity, ...
Global and China Cobalt Industry Report, 2021-2026
As a very rare metal and an important strategic resource for a country, cobalt gets typically utilized in battery materials, super heat-resistant alloys, tool steels, cemented carbides, and magnetic m...
Automotive Event Data Recorder (EDR) Industry Report, 2022
An event data recorder (EDR), sometimes referred to informally as an automotive black box, is a device or a system installed in vehicle to monitor, collect and record technical vehicle data and occupa...
Commercial Vehicle ADAS Industry Report, 2021
ResearchInChina has published the "Commercial Vehicle ADAS Industry Report, 2021", focusing on policy climate, ADAS installations, suppliers, etc., and with a deep dive into the prospects of Chinese c...
Automotive High-precision Positioning Research Report, 2022
High-precision Positioning Research: from L2+ to L3, high-precision integrated navigation and positioning will become the standard
With the development and progress of the autonomous driving industry...
China Around View System (AVS) Suppliers and Technology Trends Report, 2021 –Joint Venture Automakers
Research into JV automakers’ around view system: large-scale implementation of AVP is round the corner, and AVS vendors are energetically pushing ahead with parking fusion solution.
During January to...