The favorable policies for the autonomous driving industry will speed up the commercialization of L3/L4.
In the second half of 2023, China introduced a range of policies concerning autonomous driving, allowing L3/L4 autonomous vehicles to take to the roads legally in China. These important policies also invigorate China’s autonomous driving industry, further spur the development of technologies and business models for L3/L4 autonomous vehicles, and accelerate their large-scale commercialization.
On October 8, 2023, the Ministry of Transport of China released the Technical Guidelines for Highway Engineering Facilities Supporting Automated Driving, an industry standard that follows the development trends of digitalization and intelligence of highway engineering facilities to better meet the requirements of vehicles for autonomous driving on highways. It clarifies the standards for the construction of roadside intelligence and supporting facilities in China’s vehicle-road-cloud integration plan.
On November 17, 2023, four ministries and commissions jointly and officially issued the Notice on Piloting Access and On-road Passage of Intelligent Connected Vehicles, which makes it clear that after selection, vehicles equipped with L3 and L4 autonomous driving are allowed to trail run on roads in designated areas. It also specifies the division of responsibilities for accidents involving L3 autonomous vehicles travelling on roads.
On December 5, 2023, the Ministry of Transport of China issued the Autonomous Vehicle Transportation Safety Service Guidelines (Trial), which suggests the specific requirements for the commercial implementation of autonomous passenger and freight transport services at the national and ministerial level, mainly regulations on the arrangement of safety officers for operating autonomous vehicles.
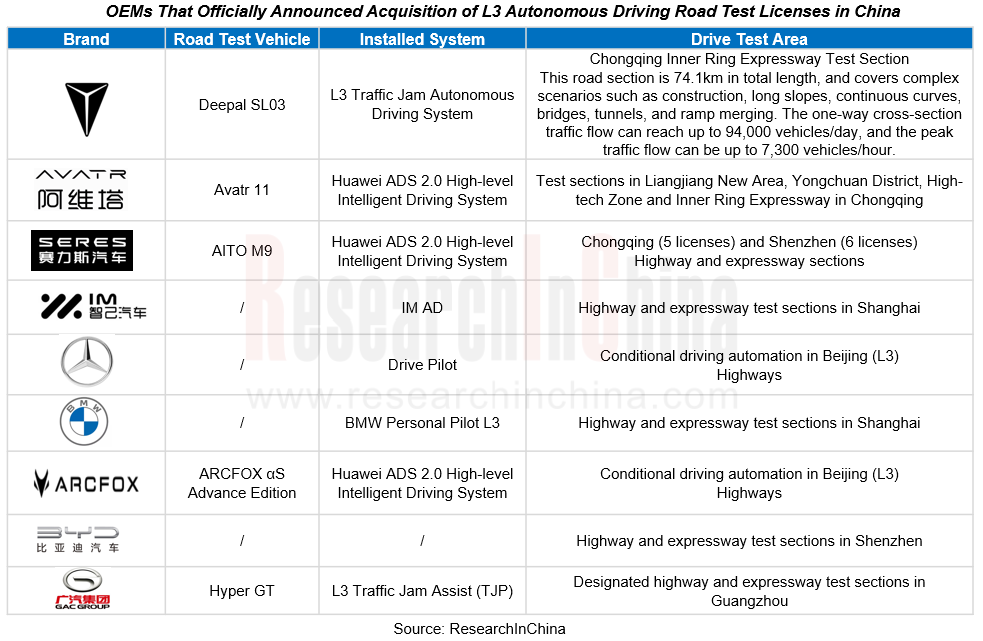
As China releases autonomous driving policies, the competition in intelligent driving is about to enter a new phase. So far, nine auto brands, including Deepal, Avatr, Seres, IM, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Arcfox, BYD, and GAC, officially announced that they had acquired L3 autonomous driving road test licenses.
L2++ reversely feeds L3/L4, and parallel strategy enables data and technology iteration.
Thanks to breakthroughs in core technologies such as chips and algorithms in the past few years, L2++ high-level driving assistance (highway NOA and urban NOA) has begun to enter a phase of large-scale promotion. This type of vehicles is very large in scale and can record a variety of complex scenarios and accumulate massive training data.
Suppliers working on L3/L4 autonomous driving, such as Baidu Apollo, Pony.ai and DeepRoute.ai, have started partnering with automakers to commercialize L2++ high-level driving assistance. On the one hand, they aim to increase business profits; on the other hand, they hope to collect road test data trained for L3/L4 use, and then enable a closed loop through autonomous driving iteration. In addition, quite a few emerging carmakers also use the L2 and L3/L4 parallel strategy to deploy high-level autonomous driving.
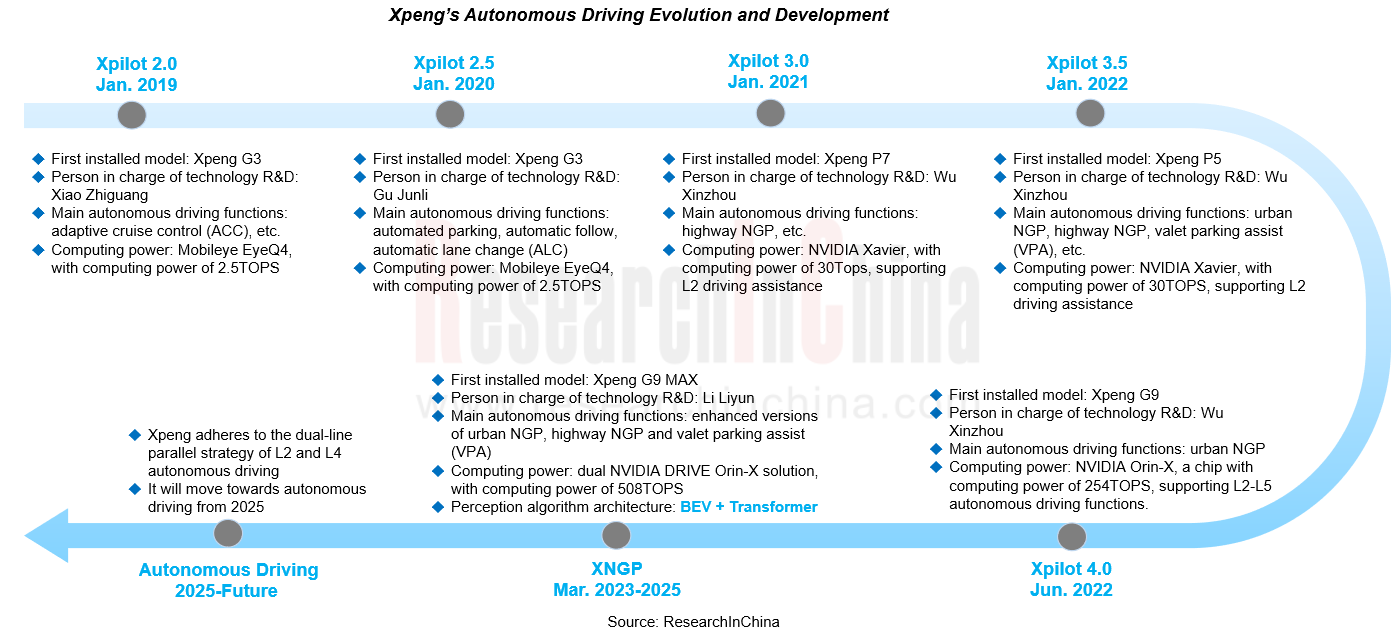
Case 1: Xpeng develops RoboTaxi and driving assistance in parallel for feedback of data and capabilities.
In Xpeng’s case, as an OEM it has started exploration of L4 autonomous driving since 2022. Xpeng G9 Robotaxi obtained the Guangzhou Intelligent Connected Vehicle Passenger Transport Test License in April 2023, and launched a pre-emptive trial experience in Guangzhou in October of the year.
Xpeng's idea for laying out L4 autonomous driving is to add Robotaxi and production vehicles with driving assistance, which are developed in parallel, to the training system to enable a two-way feedback of data and capabilities, thereby making a great leap in data collection efficiency. As production vehicles with driving assistance can collect data in multiple driving scenarios, after being fed data algorithms can iterate repeatedly and then are seamlessly put into to Robotaxi. In Robotaxi test and operation, Robotaxi forms a good synergy with driving assistance vehicles collecting data and feeds them. Both will meet each other in 2025 and enter the phase of autonomous driving.
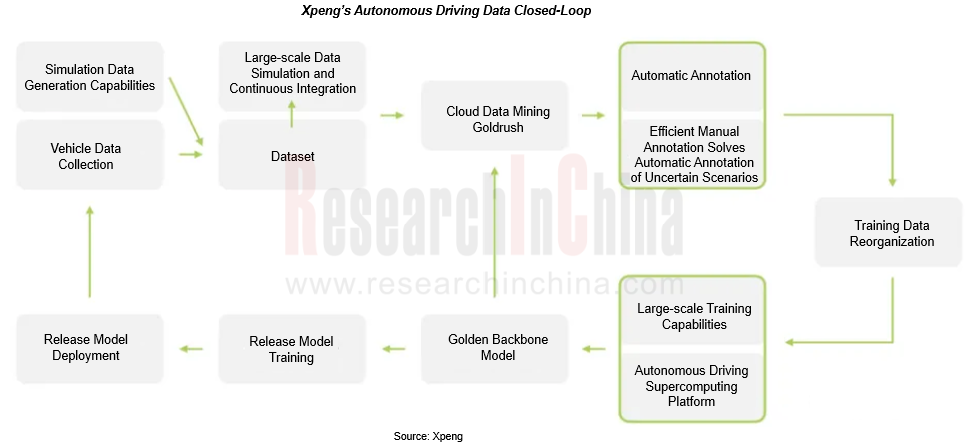
Xpeng will evolve to L4 through data closed loop and algorithm iteration. The data closed-loop and automatic annotation system are competitive edges of Xpeng in autonomous driving. Xpeng uses fleets of production vehicles to collect data, which are automatically annotated, trained by the Fuyao Autonomous Driving Computing Center and finally deployed on vehicles.
Case 2: Baidu begins to explore the L4 and L2+ symbiotic route.
In terms of L4 autonomous driving, Baidu Apollo Go has started commercial operation and testing of fully autonomous driving in Wuhan, Chongqing, Shenzhen, Beijing and other places. As of September 2023, the total safe operation and test mileage of Baidu Apollo L4 autonomous driving has exceeded 70 million kilometers, and Baidu Apollo Go has secured a total of over 3.3 million orders. As concerns L2+ driving assistance, in July 2023, Baidu Apollo ANP3.0, a NOA product, started mass production, and was first installed on Jiyue 01.
Baidu believes that the best way to commercialize autonomous driving is: in the early stage, to accumulate technologies in a designated area, and utilize dimension reduction and L4 data for hot start of L2+ products; in the later stage, to use the scale advantage of L2+ products to collect corner cases required by L4.
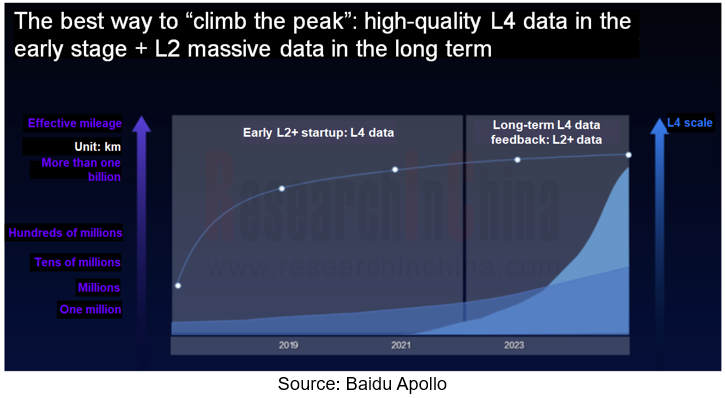
As ANP3.0 is available on market, this also means that Baidu’s plan to feed L2+ data back to L4 has officially begun to be advanced. In the follow-up, Baidu Apollo will collect corner cases via L2+ passenger cars running on urban roads, and accelerate the operation of its L4 autonomous driving system on a larger scale. According to Baidu’s plan, in 2025 its L2+ products will cross the gap with consumers, and its L4 business model will also be carried out in some areas and cities. The combination of the two will enable autonomous driving faster and more efficiently than any single way.
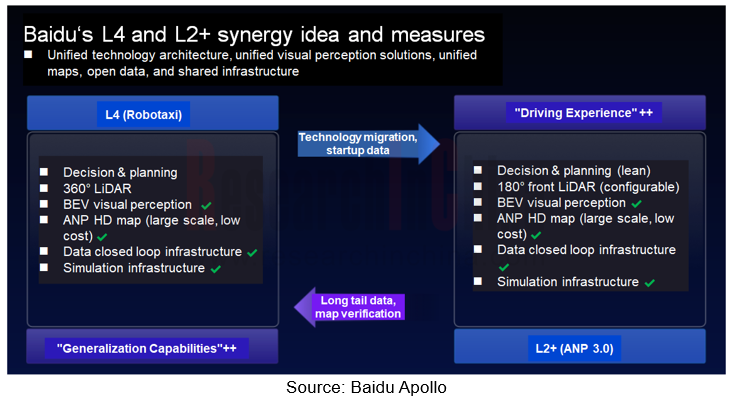
At the technology level, Baidu has achieved unified visual perception solutions, unified technology architecture, unified maps, data sharing and infrastructure sharing for L4 and L2+ intelligent driving products. L4 will keep providing advanced technology migration for L2+ intelligent driving products, and L2 data feedback will also help to generalize L4 capabilities.
As L4 Robotaxi faces setbacks overseas, how to continue to forge ahead with commercialization in China?
The commercialization of Robotaxi has been hampered at abroad. In August 2023, Waymo and Cruise were allowed to launch paid 24/7 Robotaxi services in San Francisco, California. Yet since the launch of the paid Robotaxi services, safety issues and accidents involving the operating vehicles have appeared one after another. Currently Cruise has lost its self-driving licenses in California, and has suspended all its self-driving services in the United States.
Then how to forge ahead with commercialization of Robotaxi in China? The operation of Robotaxi needs to consider how to cooperate with governments, OEMs, mobility platforms, technology companies and other parties to build an effective ecosystem. At present, in China Robotaxi players include: 1. L4 autonomous driving technology solution providers such as Baidu, Pony.ai, WeRide, and Auto X; 2. Conventional automakers like BMW and Audi, and emerging carmakers such as Tesla and Xpeng.
Robotaxi Business Model 1: "Iron Triangle".
The combination of RoboTaxi company + mobility platform + automaker is the mainstream cooperation mode in current stage. This "iron triangle" model gives full play to the respective strength of the three parties, and allows each party to be responsible for what it is best at, so that Robotaxi can be promoted faster and more efficiently, and a closed loop for the commercial implementation of autonomous driving in scenarios can be built.
As technology solution providers, Robotaxi companies enable asset-light operation. The use of OEMs’ autonomous driving platforms, vehicle design and manufacturing capabilities makes them superior in terms of mass production speed and manufacturing cost;
Mobility service operators already boast a stable user base, good mobility service experience and massive data. They have great advantages in traffic entrance, user mobility data and operation management experience. Without the traffic support of mobility platforms, Robotaxi companies will be very slow in subsequent data accumulation, which will in turn affect the quality and speed of software algorithm iterations;
OEMs with strong manufacturing capabilities can provide infrastructures and physical bases for the large-scale deployment of Robotaxi.
In addition to its own mobility platform PonyPilot+, Pony.ai also cooperates with automakers like Geely, GAC, FAW and SAIC, and is connected to OEM-backed mobility platforms such as Caocao, ONTIME, T3 Mobility, and Hongqi Smart Mobility. Pony.ai has put its Robotaxi into commercial operation. At present, Pony.ai has deployed autonomous fleets in the four cities of Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen. As of December 2023, Pony.ai has boasted a total mileage of more than 28 million kilometers of autonomous driving road tests on complex urban public roads.

In January 2024, the GAC Toyota Sienna Robotaxi model packing Pony.ai’s 6th-generation autonomous driving software and hardware system obtained the commercial demonstration operation license from Nansha District, Guangzhou. It launches paid services via Pony.ai’s own platform PonyPilot+ and ONTIME. The Robotaxi covers all of Nansha District with 803 square kilometers, and runs at 8:00-22:30 including morning and evening peak periods.
This Robotaxi model was jointly developed by Pony.ai and Toyota, and GAC Toyota was responsible for producing it. 15 units of this vehicle have been connected to ONTIME. It is also the second model that Pony.ai has joined ONTIME for mixed operation. The two parties will facilitate the large-scale commercialization of Robotaxi services by complementing each other with the "technology + platform" model.
Robotaxi Business Model 2: emerging carmakers make a foray into the field.
At present, emerging carmakers like Tesla and Xpeng have made it clear that they will set foot in the Robotaxi field. Differing from the Iron Triangle model that features a mutually binding relationship, emerging carmakers have the following superiorities in Robotaxi:
1.Great data collection capabilities to better “feed” the software system;
2.In terms of vehicle costs, OEMs have a large supply chain system, and self-production of Robotaxi makes it easy to control costs. In the case of Tesla that develops and produces a Robotaxi model fully in-house, the scale effect enables much lower production cost of the Robotaxi;
3.For OEMs, huge offline infrastructures such as sales centers, experience centers and charging networks, online user communities, and their own APPs can be always used as traffic entrances.
Utilizing their own resource system, emerging carmakers have more abilities to build their own ecosystem in Robotaxi. Their full-stack self-developed autonomous driving capabilities, large chip and sensor procurement, vehicle mass production capabilities, and massive user data will give them a bigger initiative in the competition in the Robotaxi market.

Xpeng Robotaxi, built on the model G9, is a completely OEM model with no hardware additions, and functional iterations only via software. Compared with other aftermarket Robotaxi models on market which often cost hundreds of thousands to one million yuan, Xpeng Robotaxi offers higher cost performance, making it feasible to truly and fully implement this business model in the future.
In April 2023, Xpeng G9 Robotaxi officially obtained the intelligent connected vehicle passenger transport test license of Guangzhou, covering all general test roads in the city. In the second half of 2023, the trial operation of the autonomous passenger transport services were launched for all users in Huangpu District, Guangzhou. Users can summon Xpeng G9 self-driving car via the WeChat applet. As for the final business model, Xpeng hopes to sell a hardware + software package to mobility companies, allowing them to purchase their own vehicle hardware and software.
In 2023, China's Robotaxi market had thousands of vehicles. The industry generally believes that the potential Robotaxi market can be valued at one trillion yuan in the future. Faced with such a huge potential market, players no longer craft a publicity stunt and launch a demonstration project, but work to deploy commercial Robotaxi.
In addition, Robotaxi cannot be commercialized without the support of favorable policies. In current stage, governments across China are doubling down on the Robotaxi market, and there have been more than over 30 cities introducing policies concerning intelligent connection. In January 2024, 17 departments including the National Data Administration jointly issued the Three-Year Action Plan for "Data Elements ×" (2024-2026), suggesting promoting the innovative development of intelligent connected vehicles, supporting the commercial trial operation of autonomous vehicles in specific areas and specific periods, and breaking down the data barriers between automakers, third-party platforms, transportation companies and other entities.
A new mobility ecosystem cannot be built in a short period of time. It not only requires incentive policies, but also cooperation of the entire industry to jointly advance the maturity and implementation of technologies and standards and continue exploration of mature models for commercial implementation. In the short term, Robotaxi's commercial closed loop may mainly rely on the coordinated development of mobility service operators and autonomous driving technology companies.